Ginseng and red sage reduce arterial stiffening caused by exercise
10/01/2018 / By Edsel Cook

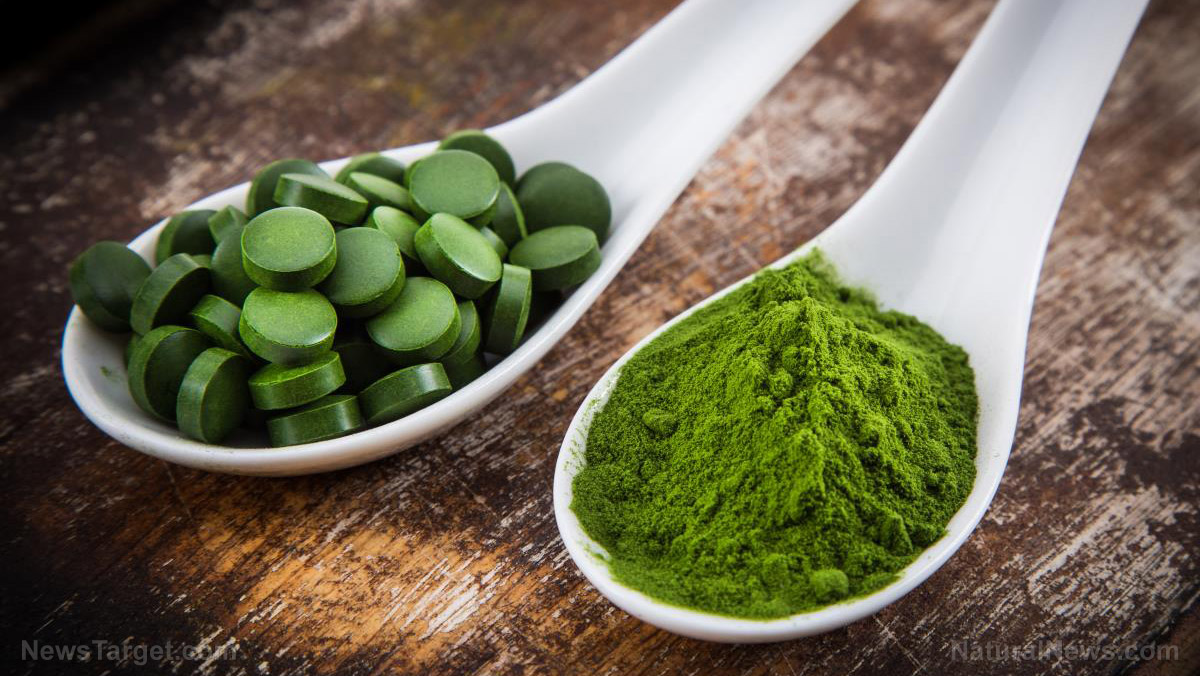
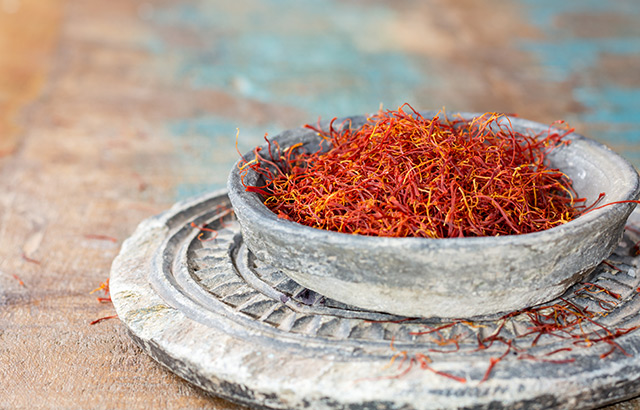
Taiwanese researchers tested the ability of two Chinese medicinal herbs to delay the onset of vascular stiffening in muscles after excessive exercise. They reported that a week-long treatment using ginseng (Panax ginseng) and red sage (Salvia miltiorrhiza) were able to improve the symptoms of arterial stiffening.
This study was conducted by the National Taiwan University. The researchers published their findings in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
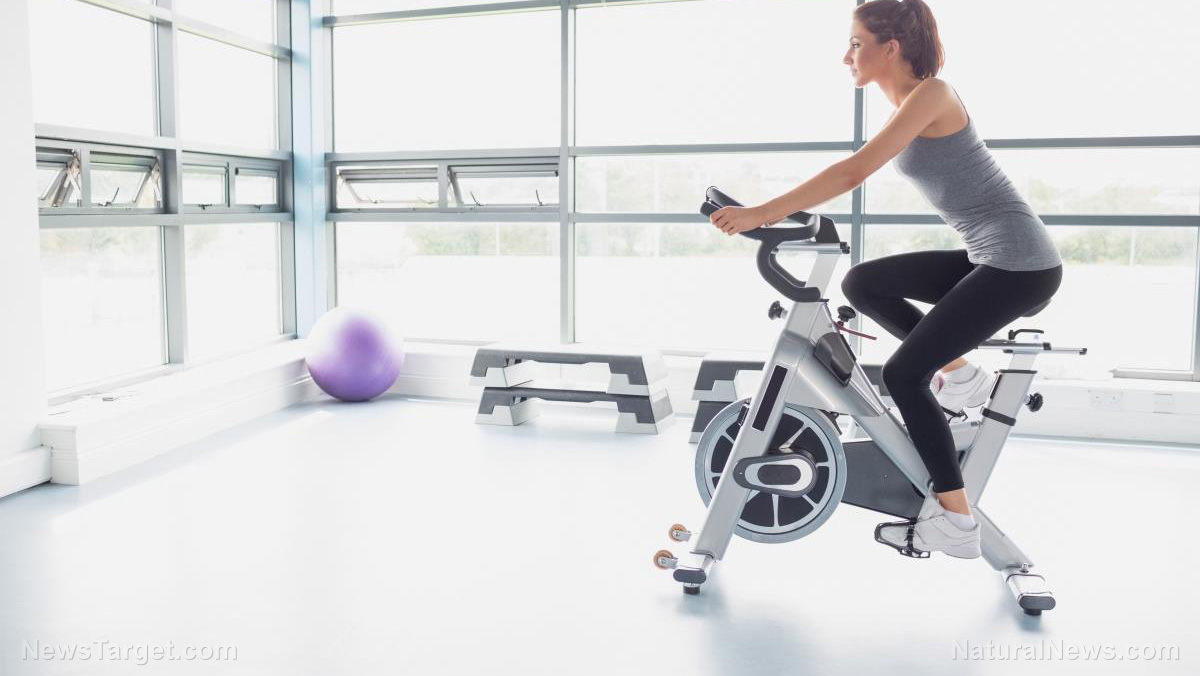
- Participants were divided into two groups, the Chinese herb group and the placebo group. Both groups went through an eccentric exercise trial and a controlled trial that involved sitting and resting. The herb group received ginseng and red sage for seven days.
- Both groups reported experiencing more muscle soreness during one or two days after the exercise. However, the herbal group recovered their active range of motion in less time than the placebo group.
- After 24 hours, the levels of plasma creatine kinase rose for both groups. The concentrations of the beneficial enzyme were higher in the placebo group.
- The placebo group showed significant arterial stiffness 24 hours after the trial. Meanwhile, the herbal group did not display an increase in stiffness.
- The levels of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 cytokine only rose in the placebo group. The increase of the cytokine was linked to the changes in arterial stiffness caused by eccentric exercise.
The results indicated that arterial stiffness caused by eccentric exercise could be reduced by taking ginseng and red sage as herbal supplements for short-term periods.
The complete study can be reviewed on this page.
If you want to learn how to use ginseng and red sage to tend to your aches and pains, visit ChineseMedicine.news.
Journal Reference:
Lin HF, Tung K, Chou CC, Lin CC, Lin JG, Tanaka H. PANAX GINSENG AND SALVIA MILTIORRHIZA SUPPLEMENTATION ABOLISHES ECCENTRIC EXERCISE-INDUCED VASCULAR STIFFENING: A DOUBLE-BLIND RANDOMIZED CONTROL TRIAL. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 6 June 2016;16(168). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1139-4.
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, arterial stiffness, Chinese medicine, eccentric exercise, exercise, exercise recovery, fitness, ginseng, herbal medicines, herbal remedies, Herbs, natural cures, natural remedies, Panax ginseng, red sage, research, traditional Chinese medicine