Substituting peanuts in your diet can help reduce consumption of unhealthy snacks
03/04/2019 / By Michelle Simmons
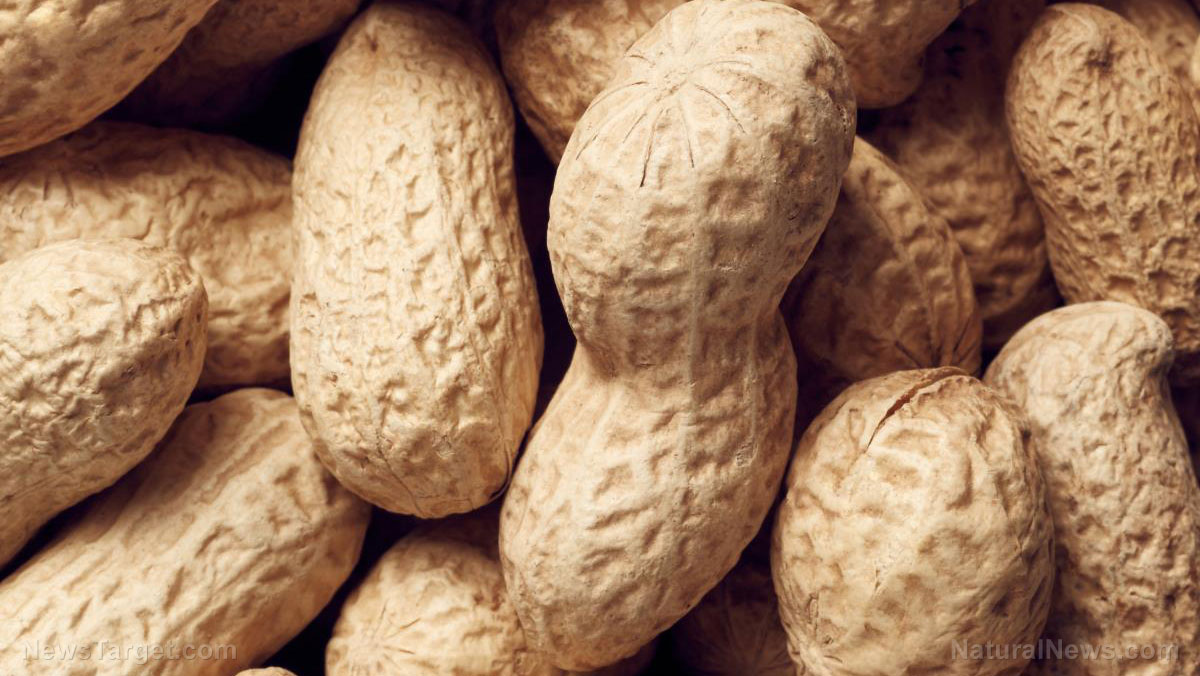

Researchers from the University of South Australia, University of Adelaide, and the University of Newcastle in Australia report that regularly snacking on peanuts instead of unhealthy foods helps improve one’s diet. They reached this conclusion after investigating the effects of adding peanuts to diet on snacking habits and energy intake.
- Snacking is associated with the intake of unhealthy foods which may contribute to the development of obesity. Peanuts can increase satiety and may aid in weight management.
- Therefore, the researchers hypothesized that peanut consumption may help reduce the intake of unhealthy snacks.
- To test this hypothesis, the researchers recruited 61 healthy participants, with a mean age of 65, who consumed their regular diet with or without peanuts for 12 weeks.
- The participants recorded their food intake in food diaries, which were analyzed by the researchers at the start and after each 12-week period for meal and snack content and timing.
- The results showed that when the participants ate peanuts, their total energy intake was higher, as well as their body weight and snacking occasions, compared with control.
- Moreover, men consumed less savory snacks during the peanut phase, while women consumed less sweet snacks.
- These results, which were published in the journal Nutrition Research, indicate that despite increased energy intake and snacking frequency, eating peanuts may improve the diet by reducing the intake of unhealthy snack foods.
In conclusion, the findings of the study suggest that eating peanuts may help improve diet by reducing the intake of unhealthy foods.
To read more studies on reducing junk food intake, visit JunkFood.news.
Journal Reference:
Barbour JA, Stojanovski E, Moran LJ, Howe PRC, Coates AM. THE ADDITION OF PEANUTS TO HABITUAL DIETS IS ASSOCIATED WITH LOWER CONSUMPTION OF SAVORY NON–CORE SNACKS BY MEN AND SWEET NON–CORE SNACKS BY WOMEN. Nutrition Research. May 2017; 41: 65-72. DOI: 10.1016/j.nutres.2017.04.005
Tagged Under: diet, eating habits, fatty foods, fightobesity, healthy diet, nuts, Peanuts, slender, sugary foods